April 16, 2024
General
Structuring Your Product Engineering Team for Growth and Scalability
Dunbar’s number posits that once an organization reaches 150 people, it hits a turning point where additional growth creates obstacles.
Atlassian’s Head of Engineering Stephen Deasy supports this idea while assuming:
“When the team has 15 people, the manager can probably physically see everyone. They can look over their monitor to talk to people and they generally know what each person is working on. At 40 people, team members are sitting on a different floor or in another building. You might have a bi-weekly sync to talk about big milestones. But when you get to 150 people, teams interact on a more transactional basis on projects, and the overall group starts to feel less like a coherent team with a shared mission.”
So how can a Head of Engineering set their team up for success regardless of its size?
In this article, we'll explore the ideal engineering team structure, highlight the common challenges faced by growing teams, reveal a size-based team structure model tailored for growth and scalability with 7 key principles for effectively scaling your team, and share a real-life example.
 It's important to note that these structures serve as guidelines and may require adaptation based on industry specifics and business needs.
It's important to note that these structures serve as guidelines and may require adaptation based on industry specifics and business needs.
Why structuring your engineering team is important
Team structuring is more than just who sits where or who reports to whom; it defines how tasks are assigned, how communications are held, and how decisions are made. In other words, this structure reflects how a team operates. A well-structured team helps to create an environment in which innovation, collaboration, and productivity thrive. On the other hand, a poorly organized team will create confusion, hurdles, and missed opportunities. By structuring your engineering team carefully, you will foster growth, scalability and, ultimately, the proper foundation for the success of your product.Key organizational gaps growing teams face
Several significant challenges stand in the way of growth and efficiency for engineering teams. Some of the most common ones are listed below.-
Communication gap
-
Alignment gap
-
Workflow gap
-
Team cohesion gap
7 principles of scalable engineering teams
When building scalable engineering teams, it's crucial to consider common pitfalls that could hinder efficiency and growth. Any manager of a growing organization should keep in mind the following 7 key principles while building a scalable engineering team.-
Align in the present
-
Nurture autonomy
-
Adopt a team-first approach
-
Balance communication
-
Avoid reorganizations
-
Measure the load
-
Build expertise within a team
Engineering team structure based on team size
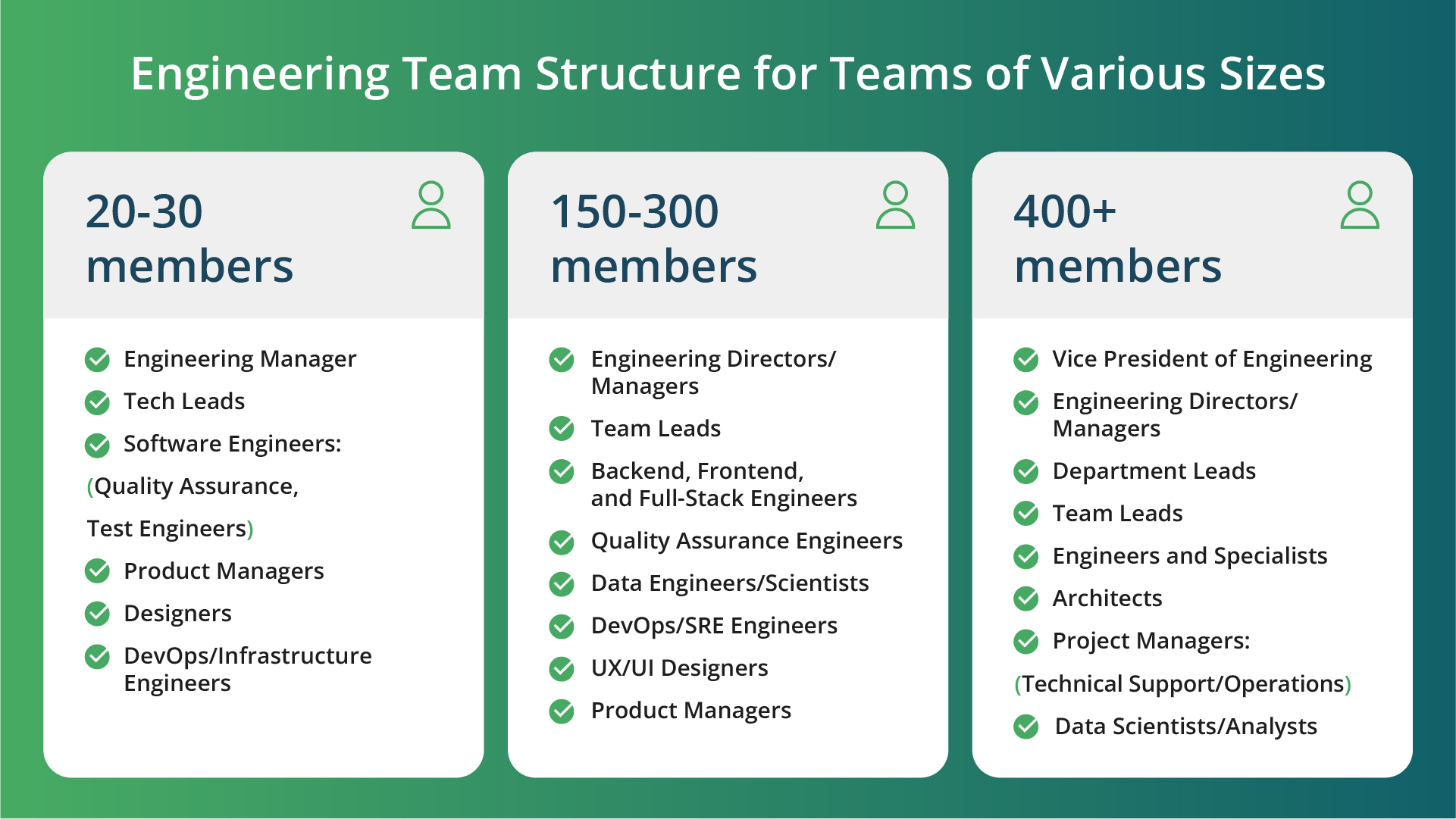
There are several team structure models that product engineering teams can adopt to support growth and scalability. Below, we will provide a size-based approach to team structuring, where each team unit is responsible for a specific product development domain.Engineering team structure with 20-30 members
- Engineering Manager - provides guidance, sets goals, and manages resources
- Tech Leads - offer technical leadership and mentorship
- Software Engineers - responsible for coding and feature implementation
- Quality Assurance/Test Engineers - focus on software testing and quality assurance
- Product Managers - collaborate on defining product requirements
- Designers - create user-friendly interfaces
- DevOps/Infrastructure Engineers - manage deployment and maintenance
Engineering team structure with 150-300 Members
- Engineering Directors/Managers - oversee multiple teams and facilitate collaboration
- Team Leads - manage day-to-day operations of individual teams
- Backend, Frontend, and Full-Stack Engineers - specialize in different aspects of development
- Quality Assurance Engineers - conduct testing and automation
- Data Engineers/Scientists - handle data pipelines and analytics
- DevOps/SRE Engineers - ensure system reliability and efficient deployment
- UX/UI Designers - design intuitive interfaces
- Product Managers - lead product planning and coordination
Engineering team structure with 400+ members
- Vice President of Engineering - oversees the entire engineering organization
- Engineering Directors/Managers - manage departments or divisions
- Department Leads - oversee specific engineering areas
- Team Leads - manage teams within departments
- Engineers and Specialists - focus on expertise areas
- Architects - provide architectural guidance
- Project Managers - coordinate projects and manage resources
- Technical Support/Operations - handle post-development activities
- Data Scientists/Analysts - utilize data for insights
 It's important to note that these structures serve as guidelines and may require adaptation based on industry specifics and business needs.
It's important to note that these structures serve as guidelines and may require adaptation based on industry specifics and business needs.
Best practices in building successful engineering teams: Netflix developer productivity engineering team
Netflix implements a sophisticated approach to engineering experience. Led by Kathryn Koehler, Director of Productivity Engineering, the company's strategy focuses on enabling developer experience (DevEx) and efficiency over mere measurement. Within Netflix's platform engineering team, consisting of approximately 450 individuals supporting over 2,500 engineers, Koehler's 80-person developer productivity engineering team plays a central role. They are responsible for enhancing the developer experience from code creation to deployment, ensuring that engineers can focus on their core responsibilities without being burdened by unnecessary complexities. Netflix's centralized platform team, comprising 150 individuals, develops tools and infrastructure to abstract away complexities, allowing developers to operate seamlessly within their domains of expertise. To streamline operations, Netflix offers internal customer support handled by a dedicated team. This support structure assists developers in navigating tools and addressing technical challenges, allowing them to remain focused on high-impact tasks while ensuring that critical issues receive prompt attention. Netflix’s example highlights the importance of clearly defined roles and responsibilities in large teams with complex products. This dynamic is a pillar of successful product development flow.Final thoughts
In this article, we covered engineering team structuring, highlighted common challenges they face, revealed various team structure models tailored for growth and scalability, and provided strategies for effectively scaling the team. By understanding the importance of team structure, anticipating common challenges, exploring various models, and implementing effective scaling strategies, you can position your team for long-term success. Kanda has extensive expertise in working with engineering teams of various sizes throughout our project endeavors. Whether it's 50 or 500 – whatever the organization size you represent, our team of experts is ready to cultivate a collaborative culture and share valuable insights on how to build a scalable team of dedicated engineers and product development experts. With over two decades of experience in custom software development, we’ve refined the formula for productive vendor-partner teams that seamlessly work together to achieve common goals. Talk to us today so we can collaborate to achieve your product development goals more efficiently.Related Articles

Comprehensive AI Security Strategies for Modern Enterprises
Over the past few years, AI has gone from a nice-to-have to a must-have across enterprise operations. From automated customer service to predictive analytics, AI technologies now handle sensitive data like never before. A Kiteworks report shows that over 80% of enterprises now use AI systems that access their most critical business information. This adoption…Learn More
Building Trust in AI Agents Through Greater Explainability
We’re watching companies leap from simple automation to an entirely new economy driven by self-governing AI agents. According to Gartner, by 2028 nearly a third of business software will have agentic AI built in, and these agents will be making at least 15% of everyday work decisions on their own. While that can significantly streamline…Learn More
Machine Learning for Fraud Detection: Evolving Strategies for a Digital World
Digital banking and e-commerce have changed how we transact, creating new opportunities for criminals. Businesses lose an estimated $5 trillion to fraud each year. The sheer number of fast-paced digital transactions is too much for older fraud detection methods. These traditional tools are often too slow and inflexible to stop today's automated threats. This new…Learn More
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC): Helping You Understand Simply and Completely
Software development is a complex and challenging process, requiring more than just writing code. It requires careful planning, problem solving, collaboration across different teams and stakeholders throughout the period of development. Any small error can impact the entire project, but Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) provides the much needed support to overcome the complexities of…Learn More

